Electrophoretic Deposition of Novel Bioactive Glasses on Dense and Porous Metal Implants for Bone Tissue Applications
Electrophoretic Deposition of Novel Bioactive Glasses on Dense and Porous Metal Implants for Bone Tissue Applications


CEDOC
Presented and defended by Salwa El Baakili on 13th May 2024
Thesis directed by: Pr. Meriame Bricha & Pr. Khalil El Mabrouk
Abstract
This study emphasizes the vital role of the connection between the implant and the bone in ensuring its stability, longevity, and integration. The research investigates the use of bioactive glass coatings on metallic substrates created through 3D printing to tackle implant instability and corrosion challenges. The goal is to enhance bioactivity, promote bone growth, prevent corrosion, and ensure mechanical compatibility.
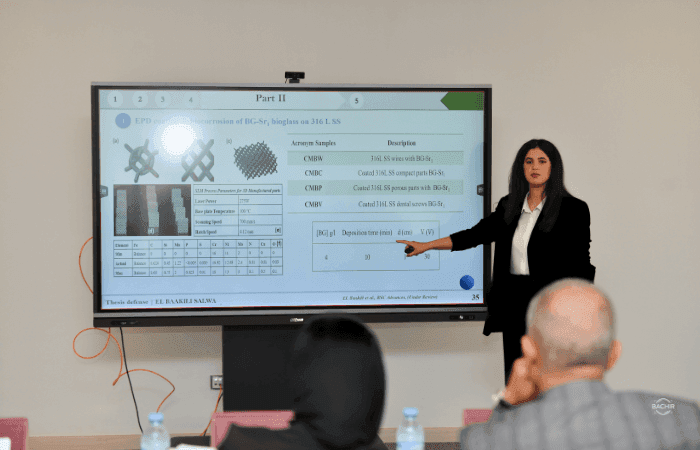
In this thesis, new bioglasses (BG) and composite coatings on 3D printed stainless steel 316L metallic parts (porous and dense using selective laser melting 'SLM') were created using the electrophoretic deposition (EPD) method. Various BG compositions were synthesized using the hydrothermal method and characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-AES), Brunauer-Emmett-Teller analysis (BET), and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). Promising results regarding bioactivity, morphology, and drug release were obtained. Incorporating ion dopants, such as strontium, magnesium, phosphorus, and chitosan, as a polymer matrix further enhanced the coatings' properties.
The strontium-doped bioactive glass 63S36C1Sr was deposited for the first time on 3D printed 316L stainless steel (SS) porous and dense structures by EPD, forming a dense, uniform, and thick layer. Similarly, the 15-7510P BG was combined with chitosan to obtain a stable suspension. The obtained BG-coated metallic parts were characterized by optical microscopy, SEM, and electrochemical corrosion behavior using potentiodynamic polarization in a Simulated Body Fluid (SBF) medium. The impact of voltage on corrosion resistance was also investigated in this study. The results showed that the corrosion resistance of 316 SS was improved by the bioactive glass 15-7510P/chitosan coating composite at 30 V.
Overall, the research demonstrates the potential of the new bioglass and the EPD technique to produce composite coatings with improved biological and anti-corrosive properties on 3D-printed porous metallic implants. These coatings would improve the implant-bone interface and ultimately enhance the lifespan of metal implants and patients' quality of life.
This thesis was defended in front of the jury members :
Full name
|
Grade
|
Institution
|
Quality
|
|
Prof. Hammouti Belkheir |
Full Professor |
Euromed University of Fes |
Jury Chair |
|
Prof. Nejjari Chakib |
Full Professor |
Euromed University of Fes |
Reviewer |
|
Prof. Lachkar Mohammed |
Full Professor |
Sidi Mohamed Ben Abdellah University, Fez |
Reviewer |
|
Prof. El Abed Soumya |
Full Professor |
Sidi Mohamed Ben Abdellah University, Fez |
Reviewer |
|
Prof. Ibn Souda Koraichi Saad |
Full Professor |
Sidi Mohamed Ben Abdellah University, Fez |
Examiner |
|
Prof. Bricha Meriame |
Associate Professor |
Euromed University of Fes |
Thesis Director |
|
Prof. El Mabrouk Khalil |
Full Professor |
Euromed University of Fes |
Thesis co-Director |
Salwa El Baakili obtained the degree of Doctor in Materials Science and Engineering, with “highest honor”.





